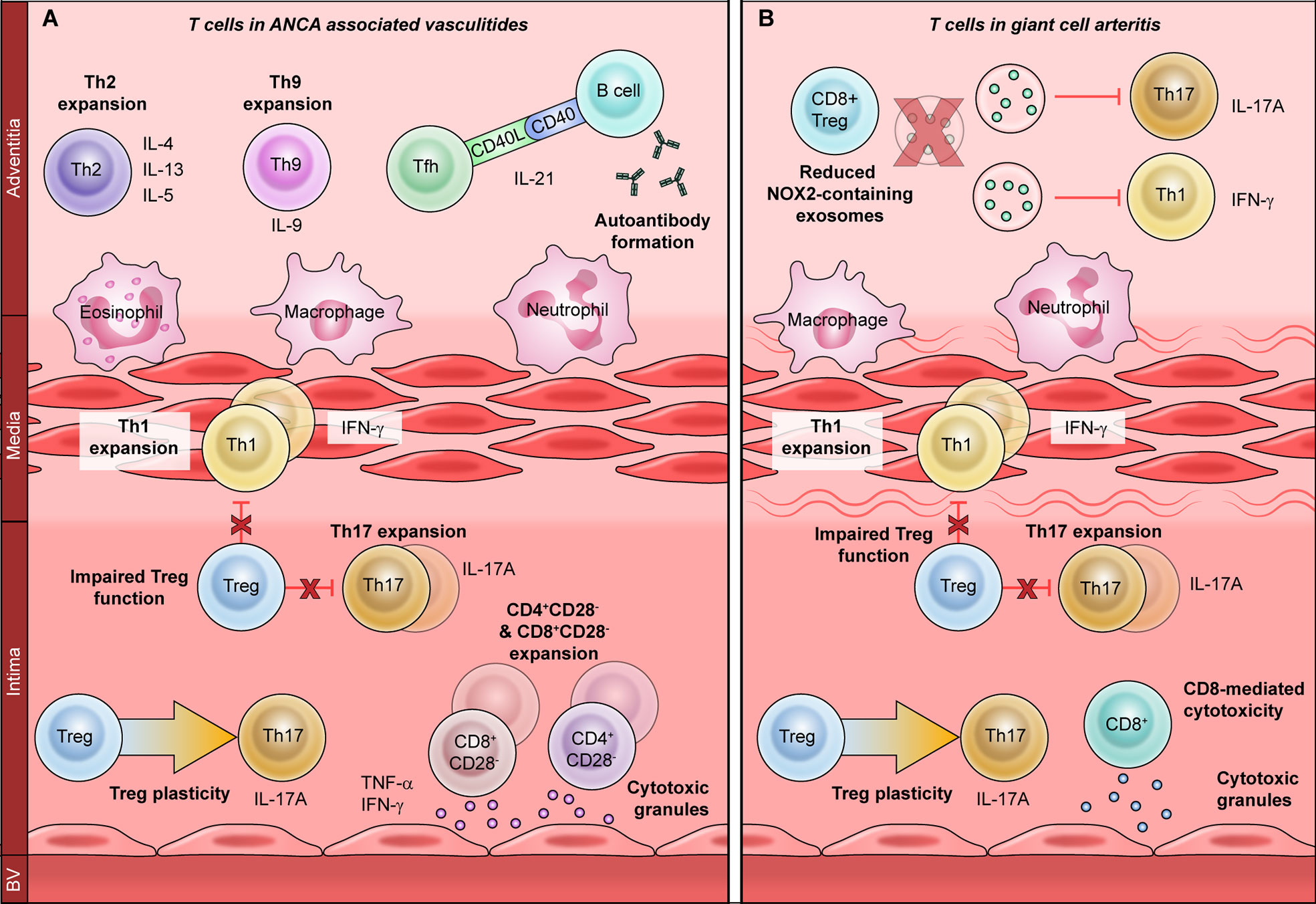
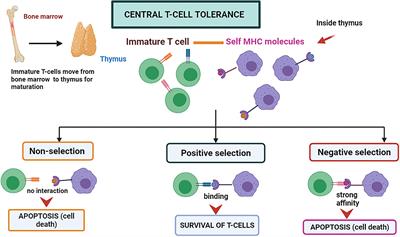
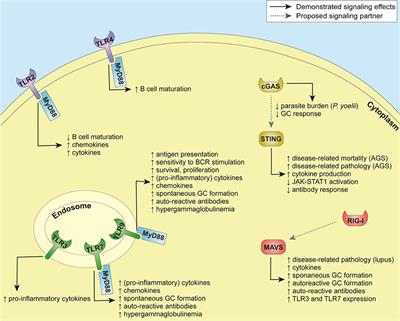
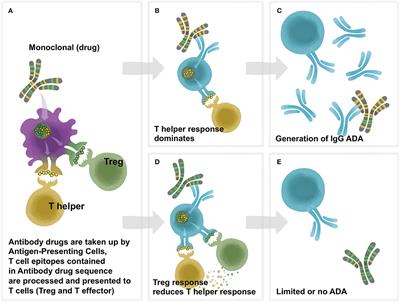
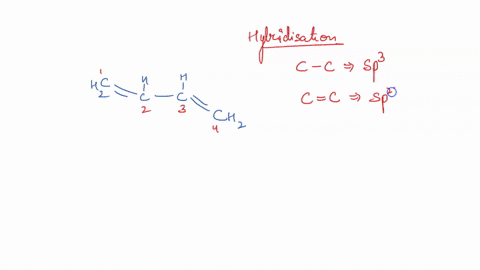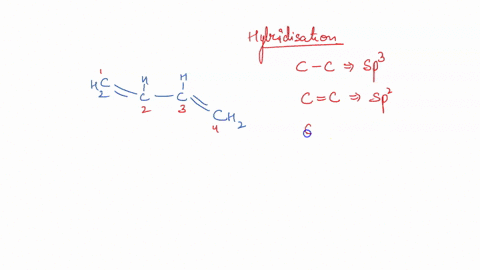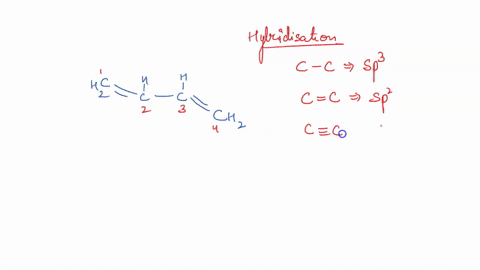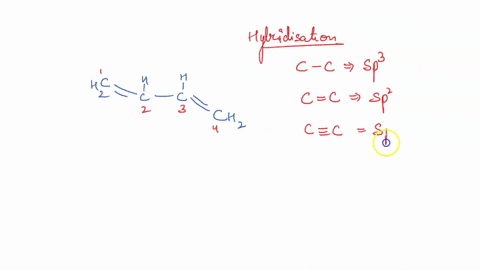
42 label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity
BIOL 1353 - Exam 4 - Mastering - Ch 17 Flashcards | Quizlet A protein molecule that forms a pore in the membranes of infected cells. ... Part B - Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity Cells Involved in Cell-mediated and Transplantation Immunity, Ii. a ... The literature concerned with the types of cells that participate in the humoral and cell-mediated immune response has been reviewed. It is postulated that the initial cells that are involved in mediating both types of immunity are functionally identical in that both are antigen-reactive cells.
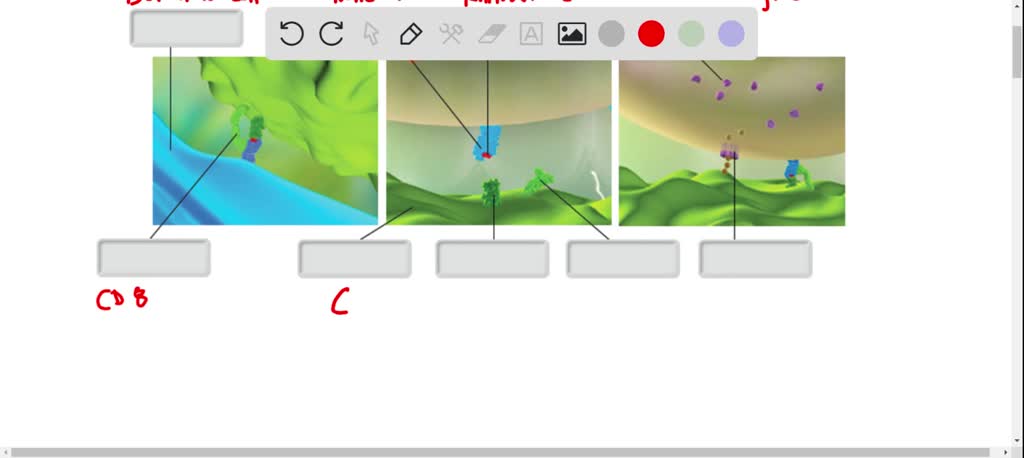
Solved Label the cells and molecules involved in | Chegg.com Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Question: Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity.
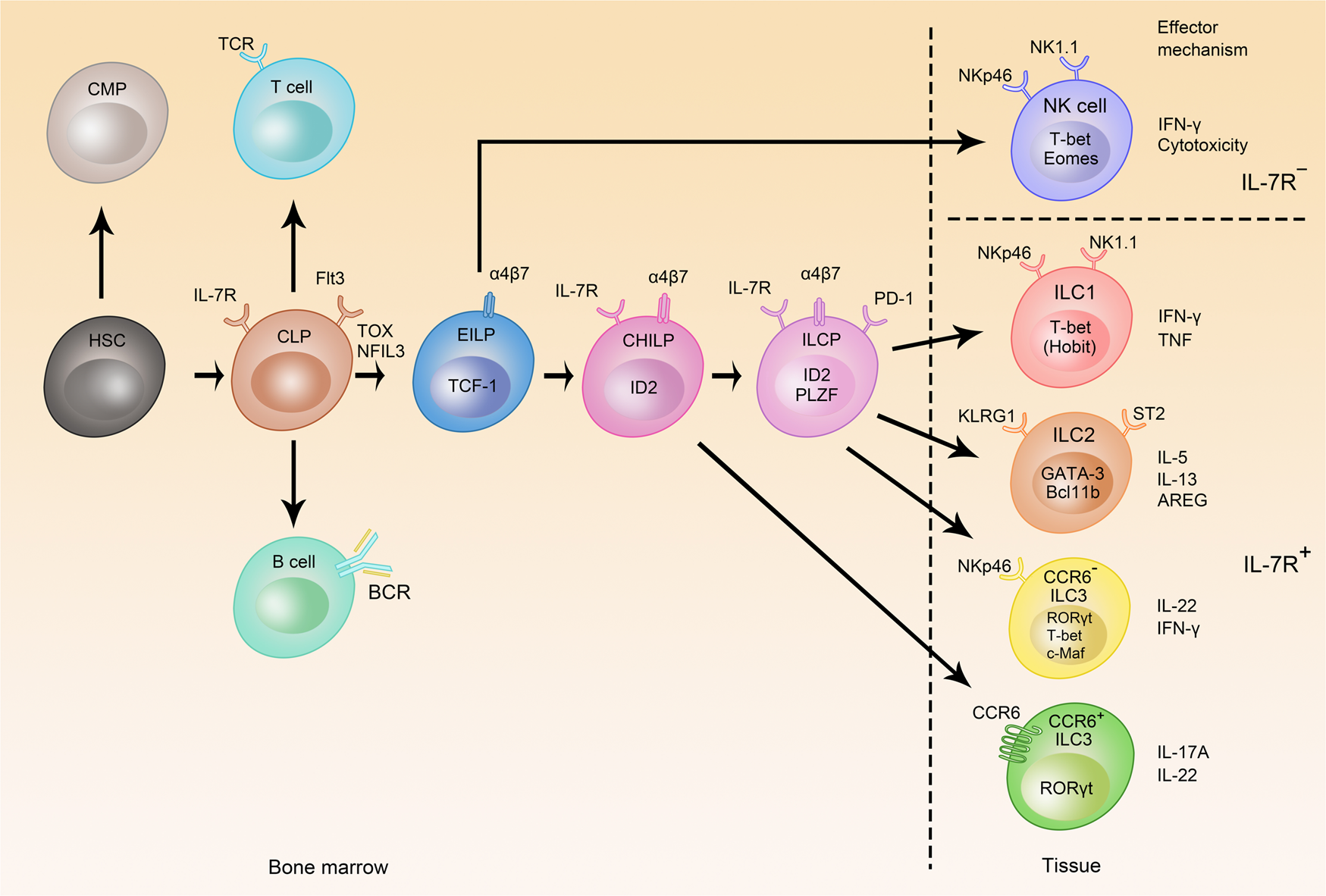
Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity
T Cell-Mediated Immunity - Immunobiology - NCBI Bookshelf To participate in an adaptive immune response, a naive T cell must first ... molecules, that synergize with antigen in the activation of naive T cells. B-Cells in Your Immune System Help Fight Off Infections - Verywell Health How B-Cells Give Us Immunity . A young B-cell, called a naive B-cell, circulates in the bloodstream, usually ending up in the spleen or lymph nodes. It gets activated by an antigen, which can be any substance the body thinks is foreign, such as a piece of a virus, or a patch of a bacterium's cutter capsule. T-cells are often involved in this ... Cells of the Innate Immune System - News-Medical.net Macrophages and neutrophils are phagocytic cells that engulf a microbial pathogen after it has been identified by the innate immune system. Macrophages are cells that are present in...
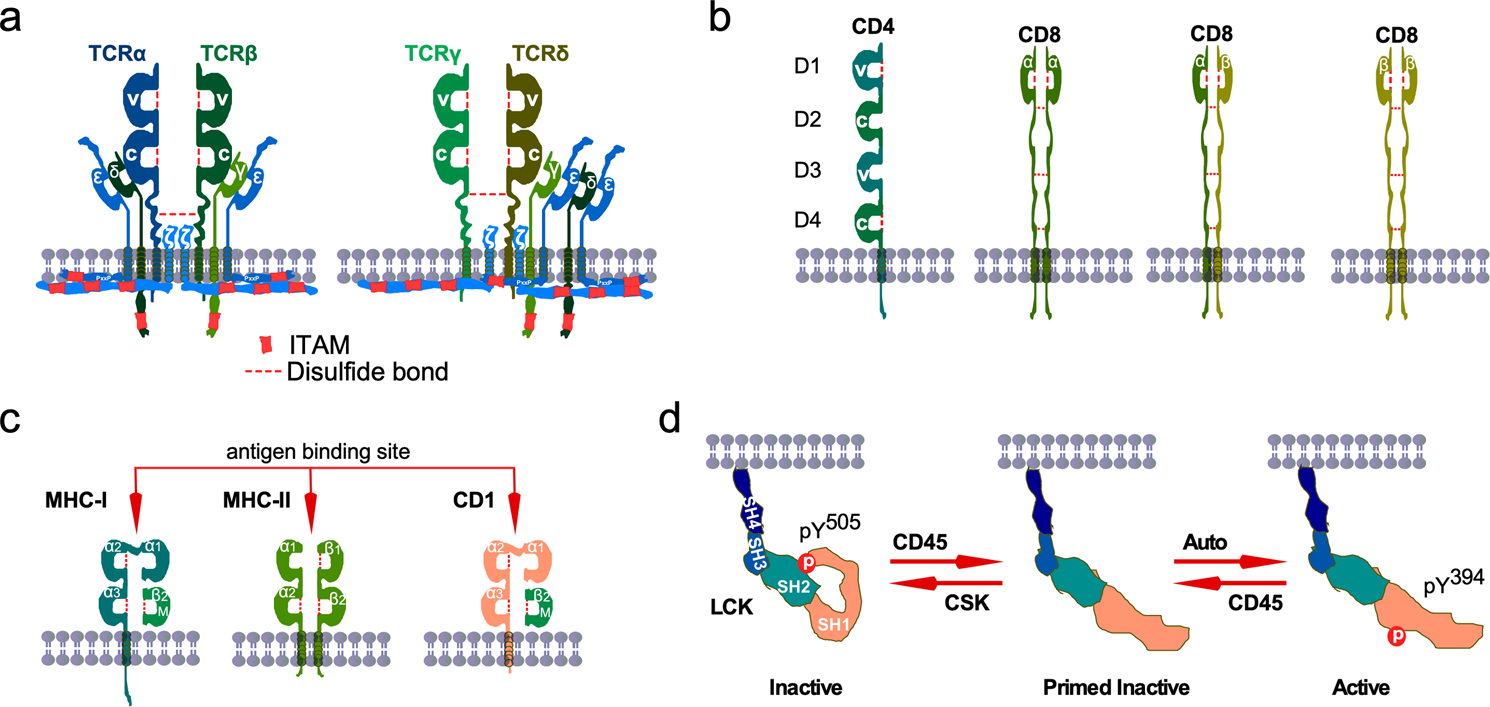
Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity. Mediators of Immune Response - PubMed Ideally, for every case the individual combination of cytokines should be recommended, which can provide stimulation or suppression of humoral and cell-mediated factors of immunity. Immunotherapy of some types of pathologies (allergy, autoimmune disorders and so on) may be based on the application of means, decreasing cytokine levels and ... Cell-mediated immunity of CD4 cells - Osmosis Once attached, the CD4 cells release molecules called cytokines which activate other immune cells to destroy the infected cell. Feedback. Questions or feedback? Understanding How Vaccines Work | CDC The immune system uses your white blood cells to fight infection. These white blood cells consist primarily of macrophages, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes: Macrophages are white blood cells that swallow up and digest germs, plus dead or dying cells. The macrophages leave behind parts of the invading germs called antigens. 14.3 T Lymphocytes and Cellular Immunity - Allied Health Microbiology For both helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells, activation is a complex process that requires the interactions of multiple molecules and exposure to cytokines. The T-cell receptor (TCR) is involved in the first step of pathogen epitope recognition during the activation process.
MHC class I - Wikipedia The α 3 -CD8 interaction holds the MHC I molecule in place while the T cell receptor (TCR) on the surface of the cytotoxic T cell binds its α 1 -α 2 heterodimer ligand, and checks the coupled peptide for antigenicity. The α 1 and α 2 domains fold to make up a groove for peptides to bind. Cell-mediated Immunity | Pathway Medicine Cell-mediated Immunity is the arm of the Adaptive Immune Responsewhich results in the generation of antigen-specific effector T-cells. A variety of effector T-cells sub-types are generated during an Adaptive Response and are responsible for either direct killing of infected cells or induction of effector functions by other immune cells. Cytotoxic T-cells: Function, Production & Activation - Cleveland Clinic Cytotoxic T-cells are one of the main types of immune cells produced in your thymus. When you have an infection, your helper T-cells activate the cytotoxic T-cells. The cytotoxic T-cells fight the infection. These T-cells are an important part of your adaptive immunity. Appointments 216.444.6503 Appointments & Locations Request an Appointment 14.1: Cell-Mediated Immunity - An Overview - Biology LibreTexts Cell-mediated immunity is directed primarily microbes that survive in phagocytes and microbes that infect non-phagocytic cells. It is most effective in destroying virus-infected cells, intracellular bacteria, and cancers. It also plays a major role in delayed transplant rejection.
Cells | Free Full-Text | C4d Deposition after Allogeneic Renal ... In the context of transplantation, complement activation is associated with poor prognosis and outcome. While complement activation in antibody-mediated rejection is well-known, less is known about complement activation in acute T cell-mediated rejection (TCMR). There is increasing evidence that complement contributes to the clearance of apoptotic debris and tissue repair. In this regard, we ... What are the Three Lines of Defense? - News Medical 18.3 T Lymphocytes and Cellular Immunity - OpenStax T cells also play a more central role in orchestrating the overall adaptive immune response (humoral as well as cellular) along with the cellular defenses of innate immunity. Figure 18.13 This scanning electron micrograph shows a T lymphocyte, which is responsible for the cell-mediated immune response. Solved Part B - Label the cells and molecules involved in | Chegg.com Expert Answer. I have pointed out …. Part B - Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity Drag the appropriate labels to their sespective targets. View Available Hint (s)
Dendritic cell subsets in cancer immunity and tumor antigen sensing ... These cells express CD64, a macrophage marker, and IRF8, a transcription factor also expressed by cDC1s, and optimally prime both CD4 + and CD8 + T-cell-mediated immunity [60, 61]. The role of ...
42.2 Adaptive Immune Response - Biology 2e | OpenStax Recall that the T cells are involved in the cell-mediated immune response, whereas B cells are part of the humoral immune response. ... They bind and engulf foreign antigens via their BCRs and then display processed antigens in the context of MHC II molecules to T H 2 cells. When a T H 2 cell detects that a B cell is bound to a relevant antigen ...
2.7 Adaptive Immunity - Human Biology - University of Minnesota Cell-Mediated Immunity: T cells. Activation of T cells also begins when T cells encounter antigens and bind to them with specific proteins on their cell surfaces, called T cell receptors. Each T cell's receptor proteins are able to bind to only one or a few very similar antigens, allowing each one to respond to different pathogens.
Humoral vs Cell-Mediated Immunity | Technology Networks The main types of lymphocytes involved in cell-mediated immunity include naïve T cells, helper T cells, killer T cells, and macrophages. Naïve T cells, which have not yet become activated, circulate in the bloodstream and the lymphatic system.
Cells involved in cell-mediated and transplantation immunity. II. A ... The literature concerned with the types of cells that participate in the humoral and cell-mediated immune response has been reviewed. It is postulated that the initial cells that are involved in mediating both types of immunity are functionally identical in that both are antigen-reactive cells.
Cell-mediated immunity - Wikipedia Cytotoxic T cells are powerful agents of cellular immunity. Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines in response to an antigen. [1] History [ edit]
The immune system: Cells, tissues, function, and disease The immune system is the body's tool for preventing or limiting infection. Its complex network of cells, organs, proteins, and tissues enable it to defend the body from bacteria, viruses,...
What Is Cell Mediated Immunity? - Video & Lesson Transcript Apr 1, 2022 ... Cell-Mediated Immune Response · T-helper cells: T-helper cells help other cells (killer T-cells, macrophages, B-cells) to stimulate immunity when ...
50.3: Cell-Mediated Immunity - Biology LibreTexts There are two types of adaptive responses: the cell-mediated immune response, which is carried out by T cells, and the humoral immune response, which is controlled by activated B cells and antibodies. Activated T cells and B cells that are specific to molecular structures on the pathogen proliferate and attack the invading pathogen.
Innate and Adaptive Immunity - American Society for Radiation ... - ASTRO Many of the cells in the innate immune system (such as dendritic cells, macrophages, mast cells, neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils) produce cytokines or interact with other cells directly in order to activate the adaptive immune system.
PDF Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity - California State University ... Adaptive Immunity: 2 kinds Humoral & Cell-mediated • Humoral immunity: mediated by antibodies circulating in the blood. -B cells • Cell-mediated immunity: -T cells Humoral Immunity B cells •are lymphocytes (leukocytes of the lymphoid lineage) • are produced & differentiate in (human) bone marrow • Subsequently, they circulate ...
Innate immunity (article) | Immune system | Khan Academy Role of phagocytes in innate or nonspecific immunity Types of immune responses: Innate and adaptive, humoral vs. cell-mediated B lymphocytes (B cells) Professional antigen presenting cells (APC) and MHC II complexes Helper T cells Cytotoxic T cells Review of B cells, CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells Clonal selection Self vs. non-self immunity
Definition of immune system - NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms
Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity ... Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Best Match Video Answer. Video Player ...
chapter 17 Flashcards | Quizlet Cellular immunity involves cells that recognize antigens and make specific antibodies against them. The primary immune response involves a slow rise in the concentration of antibodies, followed by a gradual decline. According to the animation, for approximately how many days is IgG present in the serum? Ten days
Cellular Components of the Immune System - Immunology; Allergic ... Th1 cells: In general, Th1 cells promote cell-mediated immunity via cytotoxic T cells and macrophages and are thus particularly involved in defense against intracellular pathogens (eg, viruses). They can also promote the production of some antibody classes.
Types of Immunity to a Disease - CDC
MCB 100 Homework #6 (Exam 3) Flashcards | Quizlet Put the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity in order. 1. In the lymph nodes, cytotoxic T cells encounter dendritic cells displaying epitope in MHC-I. The Tc cell is activated. 2. The active cytotoxic T cell (CTL) leaves the lymph node "looking" for infected host cells displaying the same epitope on their MHC-I.
Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity ... Nov 19, 2017 ... Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity drag the appropriate labels to their respecti… Get the answers you need, ...
Cellular Components of the Immune System - MSD Manuals Th1 cells: In general, Th1 cells promote cell-mediated immunity via cytotoxic T cells and macrophages and are thus particularly involved in defense against ...
Cell-mediated immunity of natural killer and CD8 cells | Osmosis Summary. Natural killer cells are innate lymphocytes that play a critical role in the early response to viral infection and cancer. They detect virus-infected cells and eliminate them before they can spread the infection. CD8 cells are cytotoxic T lymphocytes that recognize and kill infected or mutated cells.
The immune system review (article) | Khan Academy The main cells of the immune system are lymphocytes known as B cells and T cells. B cells are produced and mature in bone marrow. T cells are also produced in bone marrow, but they mature in the thymus. Humoral immunity Humoral immunity relies on the actions of antibodies circulating through the body.
Cells of the Innate Immune System - News-Medical.net Macrophages and neutrophils are phagocytic cells that engulf a microbial pathogen after it has been identified by the innate immune system. Macrophages are cells that are present in...
B-Cells in Your Immune System Help Fight Off Infections - Verywell Health How B-Cells Give Us Immunity . A young B-cell, called a naive B-cell, circulates in the bloodstream, usually ending up in the spleen or lymph nodes. It gets activated by an antigen, which can be any substance the body thinks is foreign, such as a piece of a virus, or a patch of a bacterium's cutter capsule. T-cells are often involved in this ...
T Cell-Mediated Immunity - Immunobiology - NCBI Bookshelf To participate in an adaptive immune response, a naive T cell must first ... molecules, that synergize with antigen in the activation of naive T cells.



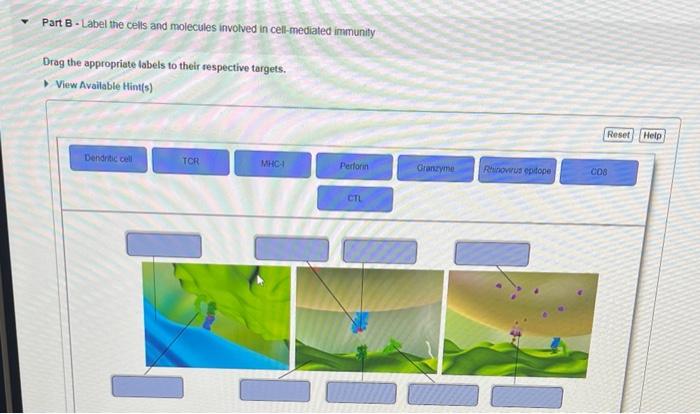




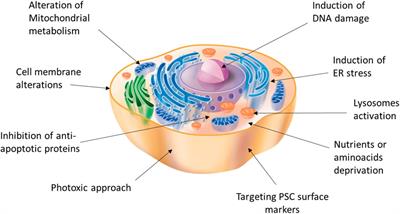


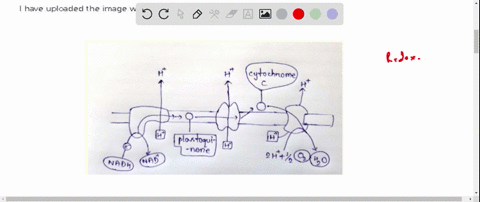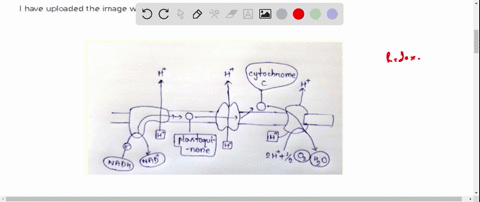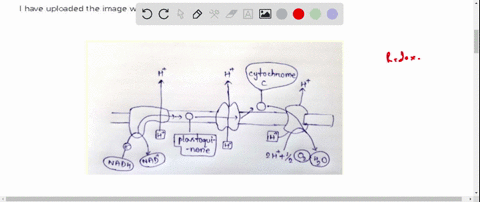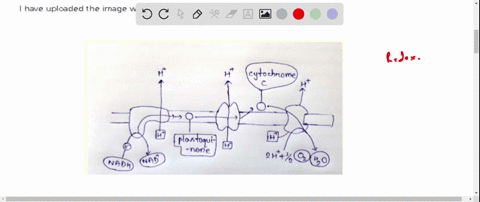
















Post a Comment for "42 label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity"